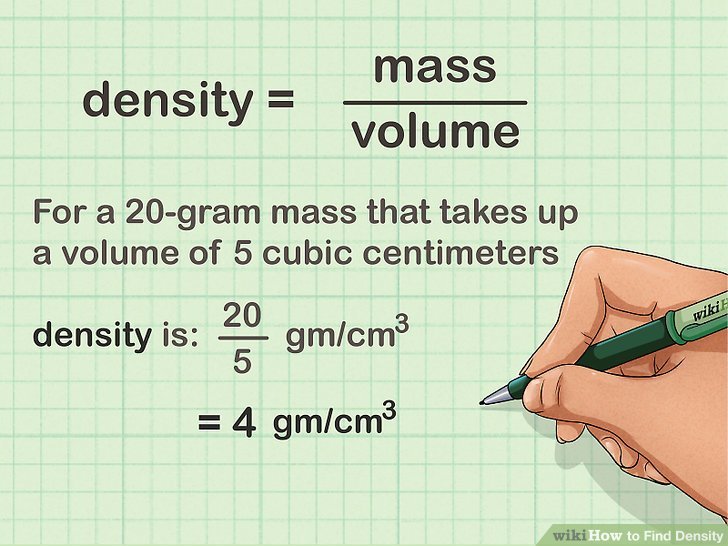How to calculate Density, a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry, is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume. It essentially tells us how “compact” or “crowded” the matter within an object is. Understanding density is crucial in various fields, from everyday life to advanced scientific research. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of density, including its definition, calculation methods, units, and real-world applications.
Definition of Density
At its core, density is the ratio of an object’s mass to its volume. In simpler terms, it’s how much “stuff” is squeezed into a particular space.
Mathematically, density is expressed as
Density (ρ) = Mass (m) / Volume (V)
Where
ρ (rho) represents density
m represents mass
V represents volume
Units of Density
The most common units for density are
Kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³): This is the SI unit for density.
Grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³): A widely used unit, especially for solids and liquids.
Grams per milliliter (g/mL): Equivalent to g/cm³ and often used for liquids.
Calculating Density: A Step-by-Step Guide
Determine the Mass
Use a balance or scale to accurately measure the mass of the object.Ensure the object is dry and free of any debris.
Determine the Volume
Regular-shaped objects: Use geometric formulas to calculate volume. For example
Cube: Volume = side³
Sphere: Volume = (4/3)πr³
Cylinder: Volume = πr²h
Irregular-shaped objects
Water displacement method
Fill a graduated cylinder with a known volume of water.Carefully submerge the object in the water.Note the new water level.The difference in water levels represents the volume of the object.
Archimedes’ principle: This principle states that the buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid1 displaced by the object. This can be used to determine the volume of irregularly shaped objects.
Calculate Density
Divide the mass of the object by its volume.
Example
Let’s say you have a block of wood with a mass of 100 grams and a volume of 200 cubic centimeters. To calculate its density
Density = Mass / Volume = 100 g / 200 cm³ = 0.5 g/cm³

Density and Its Applications
Density is a crucial property with numerous applications in various fields
Materials Science
Material identification: Different materials have distinct densities. By measuring the density of an unknown substance, it can be compared to known values to identify the material.
Material selection: Engineers and designers often choose materials based on their density. For example, lightweight materials like aluminum are preferred for aircraft construction due to their low density.
Fluid Mechanics
Buoyancy: The principle of buoyancy, which governs whether an object floats or sinks in a fluid, is directly related to density. Objects less dense than the fluid they are in will float, while denser objects will sink.
Fluid flow: Density plays a significant role in fluid dynamics, influencing factors like pressure and flow rate.
Environmental Science
Water quality: The density of water can be affected by factors like temperature, salinity, and dissolved substances. Monitoring water density helps assess water quality and identify potential pollution sources.
Atmospheric studies: Air density varies with altitude, temperature, and humidity. Understanding air density is crucial for meteorological studies and aviation.
Medical Applications
Bone density: Bone density measurements help diagnose conditions like osteoporosis, a disease characterized by low bone mass.
Body composition: Body density measurements can be used to estimate body fat percentage.
Factors Affecting Density
Several factors can influence the density of a substance
Temperature: Generally, the density of most substances decreases with increasing temperature. This is because heat causes molecules to move faster and farther apart, increasing the volume while the mass remains constant.
Pressure: Increasing pressure typically increases the density of a substance, especially gases. This is because increased pressure forces molecules closer together, reducing the volume.
Composition: The composition of a substance significantly affects its density. Different elements and compounds have unique densities. For example, the density of saltwater is higher than that of pure water due to the presence of dissolved salts.
Density and Everyday Life
Density is encountered in many aspects of our daily lives, often without us even realizing it
Cooking: When we cook, we rely on density differences. For example, oil floats on water because it is less dense.
Driving: The density of air plays a crucial role in aerodynamics, affecting the lift and drag forces on a vehicle.
Weather: Density differences in air masses drive weather patterns, such as the formation of clouds and storms.
Final Thoughts
Density is a fundamental property of matter with far-reaching implications in various fields. By understanding the concept of density and its calculation methods, we can gain valuable insights into the behavior of substances and the world around us. From the buoyancy of objects to the dynamics of fluids, density plays a vital role in shaping our environment and the technologies we use.
FAQs
What is density, and why is it important?
Density is a fundamental physical property of matter that describes how much mass is packed into a given volume.
It essentially tells us how “compact” or “crowded” the matter within an object is. Mathematically, density (ρ) is defined as the ratio of an object’s mass (m) to its volume (V): ρ = m/V. Understanding density is crucial in various fields, from materials science and engineering to environmental science and everyday life. It helps us identify materials, understand buoyancy, analyze fluid flow, and make informed decisions in various applications.
Can you provide an example of a density calculation?
Certainly! Let’s say you have a block of wood with a mass of 100 grams and a volume of 200 cubic centimeters. To calculate its density:
Density = Mass / Volume = 100 g / 200 cm³ = 0.5 g/cm³
How do I calculate the density of an irregularly shaped object?
Determine the mass: Use a balance or scale to accurately measure the mass of the object.
Determine the volume
Water displacement method:
Fill a graduated cylinder with a known volume of water.Carefully submerge the object in the water.Note the new water level.The difference in water levels represents the volume of the object.
Archimedes’ principle: This principle states that the buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. This can be used to determine the volume of irregularly shaped objects.
Calculate density: Divide the mass of the object by its volume (ρ = m/V).
To read more, Click Here